Serological diagnosis is a key method for detecting specific antibodies or antigens in blood serum or other body fluids, widely used to diagnose viral infections such as Dengue and Rift Valley Fever (RVF). This diagnostic approach relies on the immune system’s response to pathogens, where antibodies are generated to combat infection, enabling precise detection of current or past exposure.
Types of Serological Tests
In serological diagnostics, there are two primary types of tests:
-
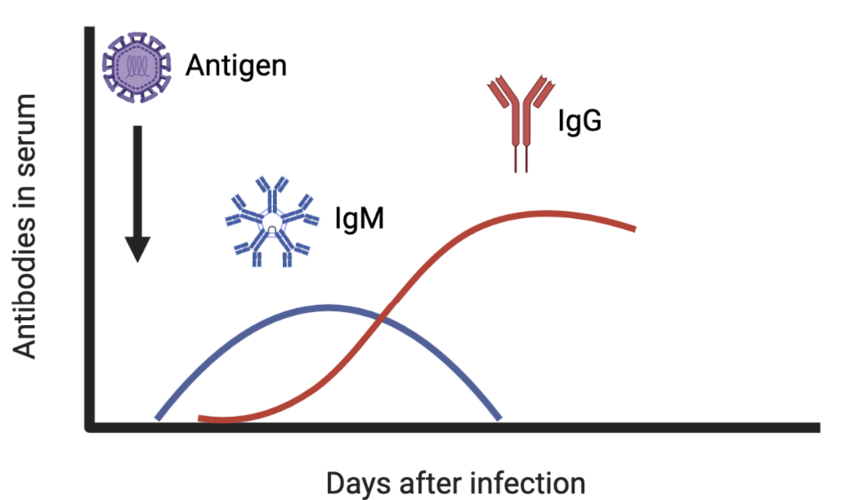
Antibody Detection: These tests identify antibodies like Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and Immunoglobulin G (IgG). IgM detection typically indicates a recent infection, while IgG indicates past exposure or long-term immunity. These tests are essential for diagnosing acute and chronic phases of diseases such as dengue and RVF.
-
Antigen Detection: These tests detect pathogen-specific antigens and are critical for identifying infections in the early stages, especially in diseases where pathogen culture is challenging.
Common Methodologies in Serological Testing
The serological tests applied in this course will focus on methods such as:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): A powerful, quantitative tool that allows for the detection of antibodies or antigens and is widely used for diseases like Dengue and RVF.
- Neutralization Tests (PRNT50, FRNT50): Highly specific assays used to quantify neutralizing antibodies, crucial for confirmatory diagnosis in viral infections.
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs): Offering a quick, qualitative approach for field-based diagnosis, these tests include Lateral Flow Immunoassays (LFIA), commonly used for detecting IgM and IgG antibodies.
This course, led by Prof. Shingo Inoue, provides both theoretical foundations and practical applications, including hands-on experience with ELISA. Participants will gain fundamental skills needed for serological diagnostics
